Stepping Stones
Goal
Condense, communicate, combine
Condense your insights into tangible representations that can be re-used in the rest of the project and help to communicate findings to the team and client.

Business Model Canvas
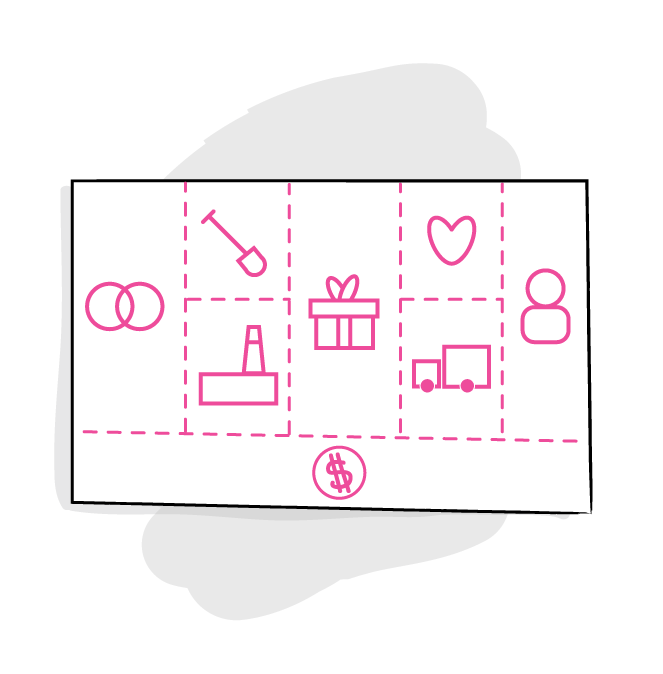
Why?
Dream up in a structured and visual way, how a new company can reach its customers and make revenues in order to understand, discuss, create and analyse a business idea.
More infoComparison Chart

Why?
A comparison chart, or comparison table, describes and compares attributes and characteristics of existing products or tools in order to determine the best option for your project.
More infoConcept
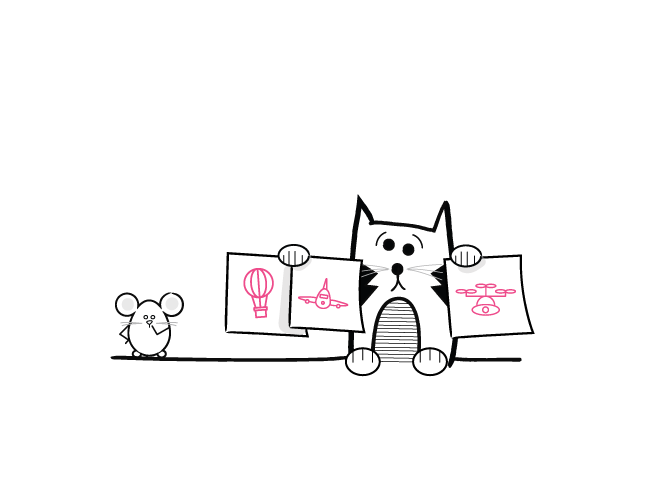
Why?
When you develop a new product or service, the concept summarizes 'the big idea' or 'the main principle' on which your solution will be based. For example, most traditional churches have a floor plan based on a cross so God can recognize a church from the sky. Validate your concept(s) with stakeholders to determine desirability and feasibility.
More infoCustomer Journey

Why?
Visualize the user experience of a service over time and across the different interaction moments (touch points) within the service.
More infoDesign Specification
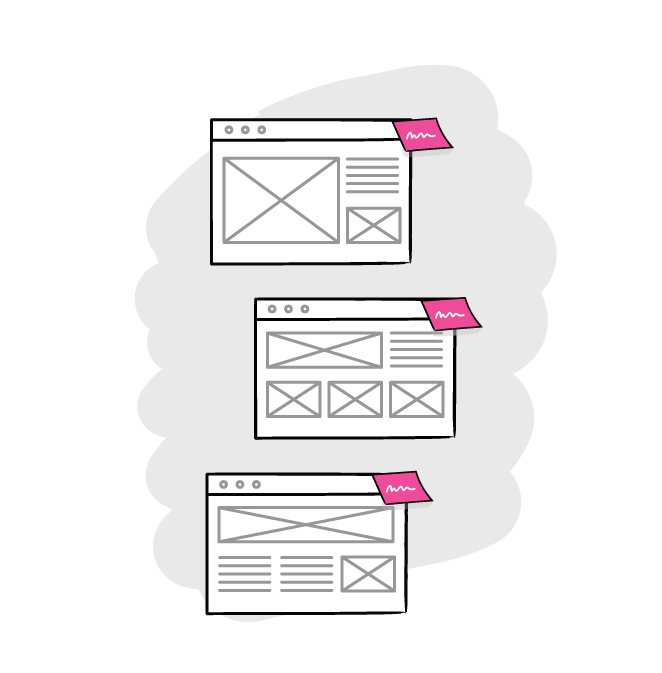
Why?
Describe the characteristics of a product, like a website or an application, in order to inform the designers and developers who are involved.
More infoEmpathy Map
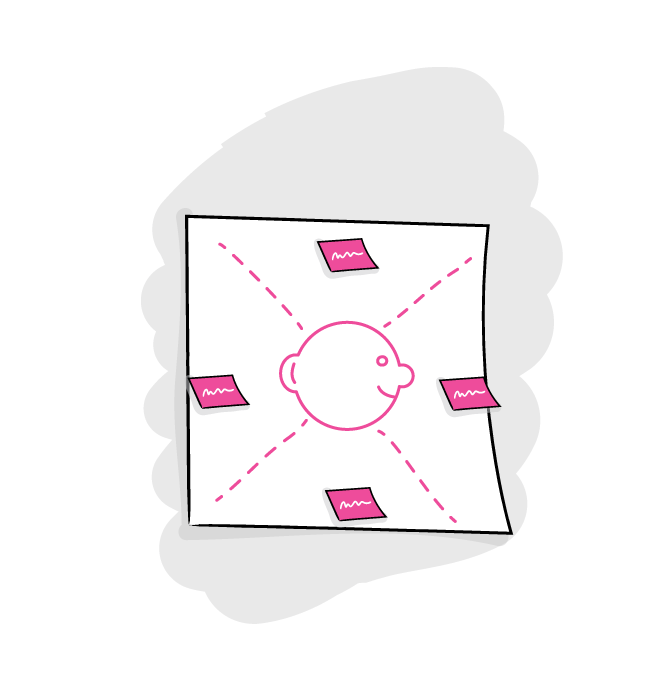
Why?
Summarize and synthetize findings from observations and interviews in a structured way. Empathy maps can offer valuable and unexpected insights in the user.
More infoInspiration Wall
Why?
Save and organize creative ideas during a project, or even permanently, in order to have access to them very quickly and let ideas 'simmer' for a while.
More infoMood Board
Why?
Before you start to make a design, a mood board can help describe the 'mood' or the 'feel' of the envisioned product.
More infoPersona
Why?
Represent the user in discussions about the design in an elegant way.
More infoRequirements list

Why?
To ensure your design meets all demands, a complete list of requirements can serve as a planning tool and checklist.
More infoScenario

Why?
Different types of scenarios exist that each serve a different purpose, for example to develop user criteria, to generate ideas or to reflect on a concept. Storyboards are a particularly common form to capture scenarios.
More infoTask Analysis
Why?
When your product has to support people performing some kind of task (for example repairing a car), a task analysis will help you and other designers understand the task better.
More info